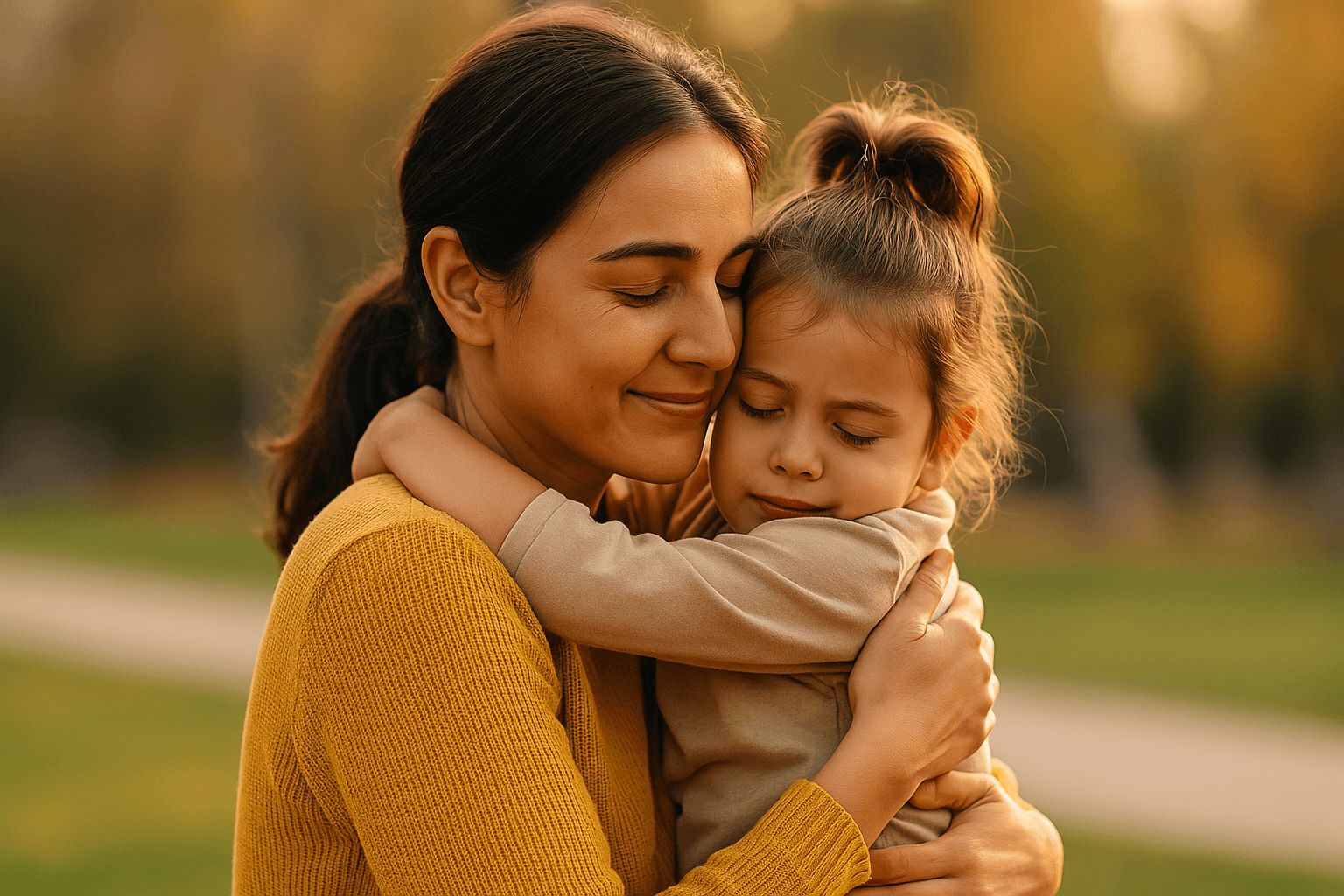Introduction:
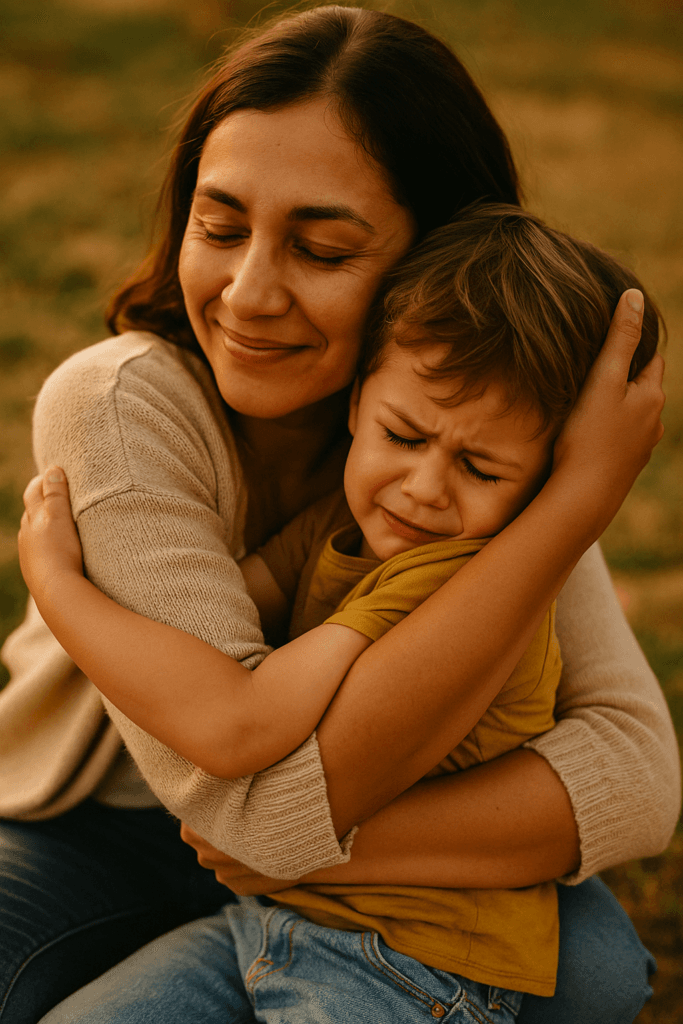

Your child is screaming.
You’re exhausted, frustrated, and maybe even embarrassed.
And your mind is racing with one desperate thought: “How do I make this stop?”
But what if the better question is:
“What is this behavior trying to say?”
Tantrums aren’t just noise. They’re neurological storms. And understanding child tantrums—through the lens of brain science and emotional development—can transform how you respond.
This blog gives you 5 game-changing insights to help you move from reaction to connection… from control to co-regulation.
Let’s decode what’s really happening behind the meltdown.
Also read – Words that make Children Feel Safe
1. Tantrums Are Not Attention-Seeking — They’re Connection-Seeking
What It Means:
When your child is losing it, they’re not manipulating you. They’re signaling distress. Their nervous system is in overload. Their body is shouting: “I feel unsafe.”
Why It Happens:
They don’t yet have the language or brain maturity to ask: “Can you help me regulate my emotions?” So instead, they cry, scream, kick, or withdraw.
What to Try:
Instead of saying, “Stop crying!” try: “I’m here. You’re safe. I’ve got you.”
Let them borrow your calm.
2. The Brain’s Logic Center Is Still Under Construction
What It Means:
The part of the brain responsible for self-control, problem-solving, and impulse management—the prefrontal cortex—isn’t fully developed until age 25.
Why It Matters:
When we say things like “Why can’t you just calm down?” we’re expecting a brain function that literally doesn’t exist yet in your child.
What to Try:
Lower your expectations in those heated moments. Your calm presence is the external regulation their internal brain is still learning to build.
Also read – 5 Transformative Conscious Parenting Exercises To Practice with Your Child
3. Tantrums Are Nervous System Overloads, Not Bad Behavior
What It Means:
During a tantrum, the child’s body floods with stress chemicals like cortisol. This activates their fight-or-flight system.
Why It Matters:
In this state, your child is not capable of “listening” or “thinking rationally.” They’re in survival mode.
What to Try:
Focus first on helping their body feel safe—soothing tone, gentle posture, fewer words. The lesson can come after the storm, not during.
Also read – 5 Tantrum Calming Exercises for Kids
4. How You Respond Wires Their Brain for the Future
What It Means:
Every time your child is upset, their brain is learning: “Is the world safe? Am I still loved when I’m struggling?”
Why It Matters:
If we respond with anger, threats, or shame, the brain encodes fear. If we respond with calm and presence, it encodes safety and resilience.
What to Try:
Stay close. Say: “You’re having a big feeling. I’m not going anywhere.”
Over time, your presence becomes the model for their future self-regulation.
5. Repair After a Tantrum Builds Emotional Safety
What It Means:
The moment after the tantrum is golden. It’s the moment where your child is calm enough to receive love, guidance, and safety.
Why It Matters:
Repair teaches your child: “Even when things get hard, we find our way back to each other.” This builds trust—not just in you, but in relationships and emotions as a whole.
What to Try:
Say: “That was really hard, huh? I love you no matter what.”
Hug, draw together, or just sit silently—whatever rebuilds the bridge.
Closing Reflection:
Understanding child tantrums isn’t about fixing behavior.
It’s about decoding emotion. About knowing that underneath every outburst is a small, overwhelmed nervous system asking: “Am I still safe with you?”
The goal isn’t to prevent all tantrums. It’s to walk your child through them—with grace, patience, and presence.
Because in the end, it’s not the tantrum that defines the moment.
It’s the connection that follows.
Scripted India by The Logic Stick is more than a podcast, it’s a conscious parenting and emotional wellness movement. Through expert-backed insights, healing tools, and real conversations, we help parents, educators, and curious minds reshape how India nurtures its next generation.