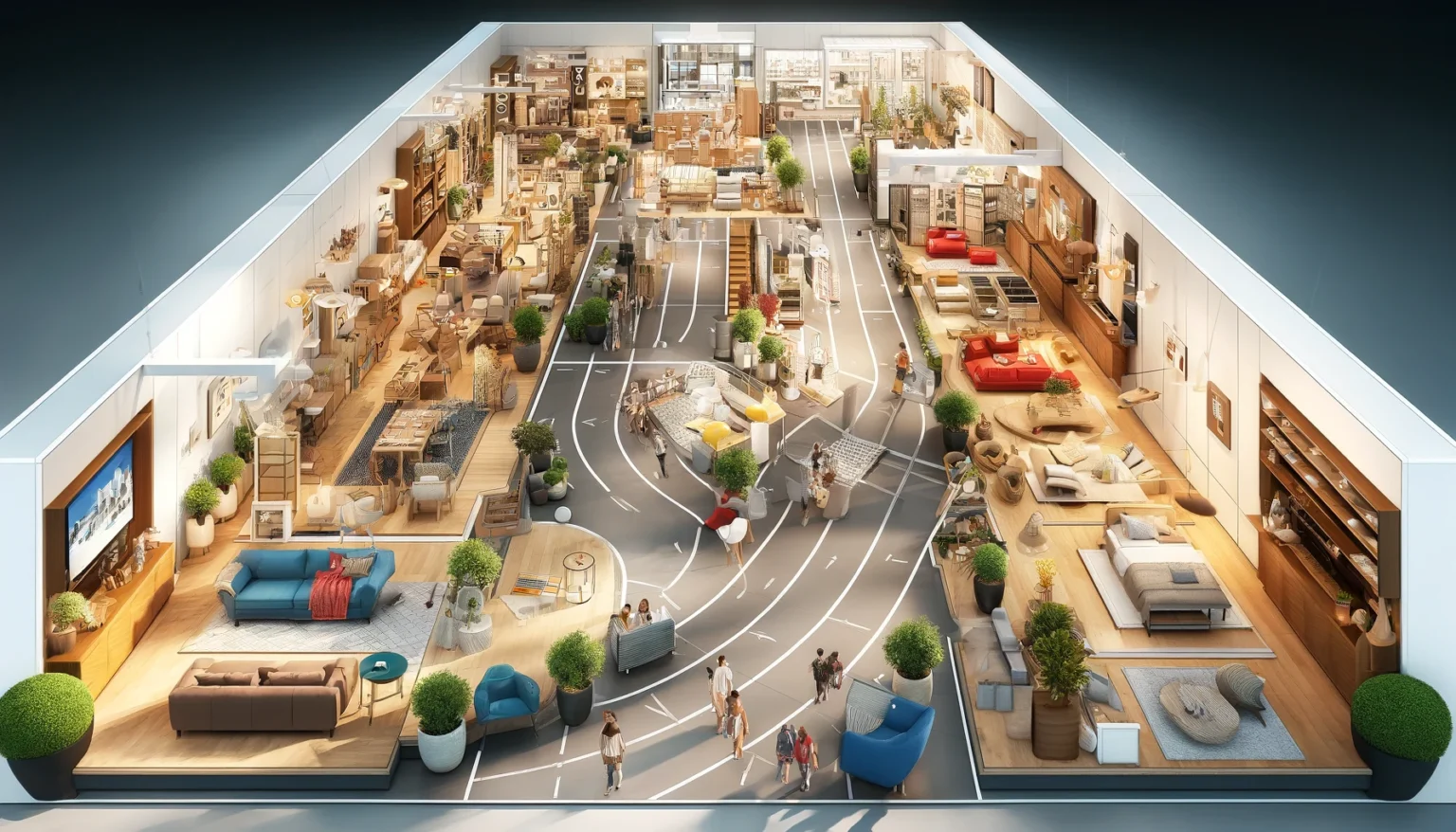
IKEA, as one of the world’s leaders in home furnishings, has ideally come up with the store design that largely capitalizes on consumer behaviors; this has largely increased the level of impulse purchases. Research indicates that over 50% of purchases in retail are unplanned.

This is what IKEA applies in their operating model of the design of their stores using a “racetrack layout.” In this layout, customers are propelled through a predetermined path and, along the way, they pass all the way through the full range of products, thereby showing customers to different items and provoking more purchases.
The aesthetic of the store, which looks much like a tastefully done-up home, is said to play a critical role in extending the duration of customers’ visits. This doesn’t just upgrade the shopping experience but will also do something with the impulse to have such pretty aesthetics at home and therefore to make purchases.
Targeting the Middle-Class with Cost-Effective Solutions
The company has appropriated its position to make its brand accessible to the middle class by creating simulated homeliness and invitingness in their stores. This environment, coupled with products that are priced competitively, appeals much to the budget-minded consumers who do not like trading style and quality with saving money.
Price-Driven Product Development
The pricing of products is one of the sensitive areas in IKEA business strategy. The firm has developed a unique way whereby the prices of products are set before carrying out the design process, hence assuring quality while aiming at a cost-effective process of manufacturing. Antonella Pucarelli, Chief Commercial Officer of IKEA Retail U.S., stresses the brand’s focus on “democratic design,” where functionality, aesthetics, and quality at reasonable prices are combined.
Sustainable and Cost-Effective Production
IKEA’s furniture, made from materials ranging from solid wood to particleboard, underscores the brand’s dedication to affordability and sustainability. Flat-pack shipping brings the transportation cost to a significant minimum. It also offers an assembly experience to the customers while saving on labor cost and marching to the changing consumer preference for DIY products.
Security of Our Customers and Their Belongings: An Assurance
Through a lot of difficulties, such as the time that its dressers faced recalls due to the senseless deaths caused by them from falling on children, IKEA has proactively sought to address any issues of concern with safety by giving out free anchoring kits and offering refunds to make sure it maintains the customers’ trust.
Customer-Centric Marketing: The Core Strategy
The global marketing strategy of IKEA is hinged on very strong customer-centric values. Respectively, the company invests in customers’ research, with the aim of tailoring products and marketing in response to the diverse needs and fashions of their clientele. This way, it increases not just satisfied customers but brand loyalty in its huge global market.
IKEA’s business ethics revolve around several core principles and practices that are integral to the company’s brand identity and operational framework. Here are some key aspects:
- Sustainability: IKEA aims to have a positive impact on the planet. This is reflected in its use of sustainable materials and resources, commitment to renewable energy sources, and efforts to reduce its ecological footprint across the manufacturing and supply chain processes.
- Social Responsibility: The company focuses on social responsibility by supporting human rights and taking a strong stance against child labor. They work towards creating better living conditions and economic opportunities in the communities where they operate.
- Democratic Design: A term coined by IKEA, “democratic design” refers to the idea that good design should be accessible to everyone, not just the wealthy. This approach combines form, function, quality, sustainability, and low prices.
- Employee Relations: IKEA places a high value on its employees, promoting a supportive and inclusive work environment. The company’s culture encourages personal growth, equality, and respect for individual values.
- Customer Centricity: Ethical conduct towards customers is central to IKEA’s philosophy. This involves providing safe, quality products, being transparent about product sourcing and materials, and ensuring good customer service.
- Community Engagement: IKEA is known for investing in local communities, whether it’s through charitable donations, community projects, or supporting local economies by sourcing from local suppliers where possible.
- Product Safety and Compliance: IKEA is committed to ensuring that all products are safe for use and comply with all legal standards and regulations. They actively work to rectify any issues that arise post-sale, as demonstrated by their product recall and safety policies.
- Fair and Ethical Business Practices: IKEA strives to maintain high ethical standards in its business practices, which includes fair treatment of suppliers and maintaining an anti-corruption policy.
It’s important to note that, like any large corporation, IKEA’s practices are sometimes scrutinized and challenged. The company is known to engage in continuous improvement in response to such challenges, seeking to uphold its reputation for ethical business practices.